
Understanding ceteris paribus
Ceteris paribus is a Latin term that is commonly used in economics, which translates to “all other things being equal.” It is an important concept that economists use to analyze the relationships between different economic variables. The concept of ceteris paribus is used to isolate the effect of a single variable on a given outcome, assuming that all other factors remain constant. In other words, it is used to analyze the relationship between two variables while holding all other factors constant.
Concept of Ceteris Paribus in Economics
In economics, ceteris paribus is used to make assumptions about the real world. This is because the real world is often too complex to understand and analyze all of the factors that influence a particular economic outcome. By assuming that all other factors are constant, economists can focus on the relationship between two variables and make predictions about the likely outcome of changes in those variables.
Real-life examples of ceteris paribus
Real-life examples of ceteris paribus can be seen in many different contexts.
For example, consider the relationship between the price of gasoline and the amount of driving people do. If we assume that all other factors, such as income and the availability of public transportation, remain constant, we can predict that an increase in the price of gasoline will lead to a decrease in the amount of driving people do. This is because people will be less willing to pay the higher price for gasoline and may choose to drive less or switch to more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Another real-life example of ceteris paribus is the relationship between the minimum wage and employment.
If we assume that all other factors, such as the state of the economy and the availability of skilled labor, remain constant, It can be anticipated that a rise in the minimum wage would result in a reduction in employment. This is because employers will be less willing to hire workers at the higher wage, and may choose to automate certain tasks or outsource jobs to lower-wage countries.
Key Points About Ceteris Paribus
- In practice, it is unrealistic to assume that “all other things are equal” in any scenario.
- All other things being equal” or “holding all other factors constant
- Ceteris paribus is a Latin term that conveys the meaning of “all other things being equal.”
- In economics, it serves as a brief way of indicating how one economic variable affects another, assuming all other variables remain unchanged.
- Ceteris paribus is widely used by economists to describe market tendencies and to construct and evaluate economic models.
- The primary obstacle with ceteris paribus is the difficulty of keeping all other variables constant to identify the cause of changes.
Ceteris paribus and economics laws
No law can be proved: In Economics, Ceteris Paribus is one of the basic economics concepts. No law, such as the Law of Demand and The Law of Supply, or any other Law in Economics can be proved if the condition of Ceteris Paribus is not applied to that specific law.
Economic laws, such as the law of supply and demand, also rely on the concept of ceteris paribus. The law of supply and demand states that the price of a good or service will be determined by the interaction of supply and demand in a market. However, this assumes that all other factors, such as government regulations and taxes, remain constant. If these factors change, the relationship between supply and demand may also change, and the price of the good or service may be affected.
Ceteris paribus and law of demand
Ceteris paribus in relation to Law of demand means that all other factors that affect demand, such as income and prices of related goods, are held constant, while only the price of a good changes to observe the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Demand Curve
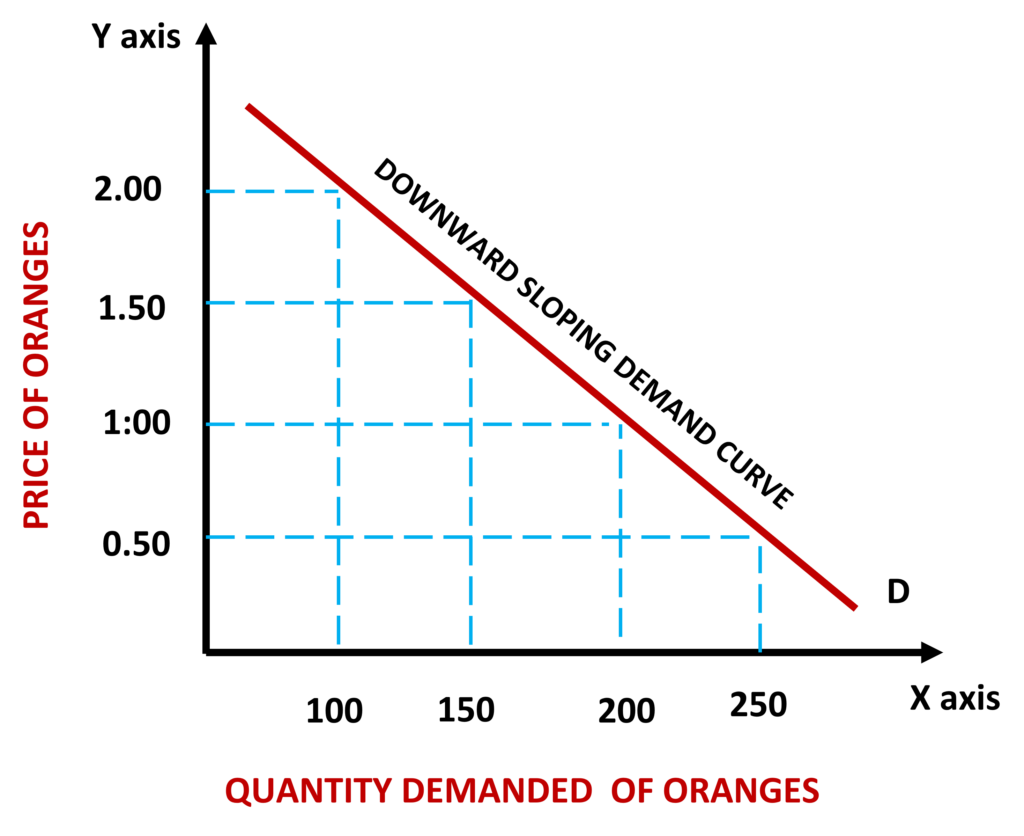
If you observe closely in the demand curve, only two variables are moving, PRICE and QUANTITY DEMANDED. And it is assumed that all other variables which may impact the price, or the quantity demanded are made constant and those variables are, the taste of consumers, the income of consumers, the price of substitute goods or products, government rules and regulations, environmental factors, and anything which can have significant or a minimal effect on the price or the quantity demanded of a good is unchanged when the law is being discussed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ceteris paribus is an important concept in economics that allows economists to analyze the relationship between different economic variables while holding all other factors constant. Real-life examples of ceteris paribus can be seen in many different contexts, from the relationship between the price of gasoline and the amount of driving people do to the relationship between the minimum wage and employment. Economic laws, such as the law of supply and demand, also rely on the concept of ceteris paribus to make predictions about the likely outcome of changes in different economic variables.
References with details
- “Principles of Economics” by N. Gregory Mankiw – This is a popular introductory economics textbook that explains the concept of ceteris paribus and its applications in economic analysis.
- “Microeconomics” by Robert S. Pindyck and Daniel L. Rubinfeld – This book is a comprehensive introduction to microeconomics and includes discussions of ceteris paribus and its use in economic modeling.
- “Macroeconomics” by Paul Krugman, Robin Wells, and Kathryn Graddy – This textbook covers macroeconomic theory and includes discussions of ceteris paribus in the context of analyzing the relationships between different economic variables.
- “Intermediate Microeconomics: A Modern Approach” by Hal R. Varian – This book is an intermediate-level microeconomics textbook that includes discussions of ceteris paribus and its use in economic analysis.
- “Managerial Economics and Strategy” by Jeffrey M. Perloff – This textbook focuses on the applications of microeconomic theory in business decision-making and includes discussions of ceteris paribus and its use in analyzing the relationships between different economic variables.
- “Econometrics: A Modern Approach” by Jeffrey M. Wooldridge – This book is an introduction to econometrics, which is the use of statistical methods to analyze economic data. It includes discussions of ceteris paribus in the context of regression analysis and other econometric techniques.
